pacman::p_load(sf, tmap, sfdep, tidyverse)In Class Ex 6: Spatial Weights
Setup
Install and load R packages
Importing data
Aspatial data | Attribute table
As tibblr
hunan2012 <- read_csv("data/aspatial/Hunan_2012.csv")Geospatial data
st_read( ) is an sf function. Import Hunan shapefile into R as an sf dataframe.
hunan <- st_read(dsn = "data/geospatial",
layer = "Hunan")Reading layer `Hunan' from data source
`C:\zoe-chia\IS415\In-class_Ex\In-class_Ex06\data\geospatial'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Data cleaning
Combine both dataframes with left join
One is tibblr, one is sf, which has a geometric column. The left data frame should be the sf dataframe with geometric data.
We use the left_join function of dplyr. The function automatically joins by the common column, “County”.
Make sure to check that the “County” columns in both dataframes have the same structure.
hunan_GDPPC <- left_join(hunan, hunan2012) %>%
select(1:4, 7, 15)Exploratory Data Analysis
Plotting Choropleth Map
tmap_mode('plot')
tm_shape(hunan_GDPPC) +
tm_fill("GDPPC",
style = "quantile",
palette = "Blues",
title = "GDPPC") +
tm_layout(main.title = "Distribution of GDP per capita by district, Hunan Province",
main.title.position = "center",
main.title.size = 0.8,
legend.height = 0.30,
legend.width = 0.25,
frame = TRUE)+
tm_borders(lwd = 0.1,
alpha = 0.6) +
tm_compass(type="8star", size = 2) +
tm_scale_bar() +
tm_grid(alpha = 0.2) 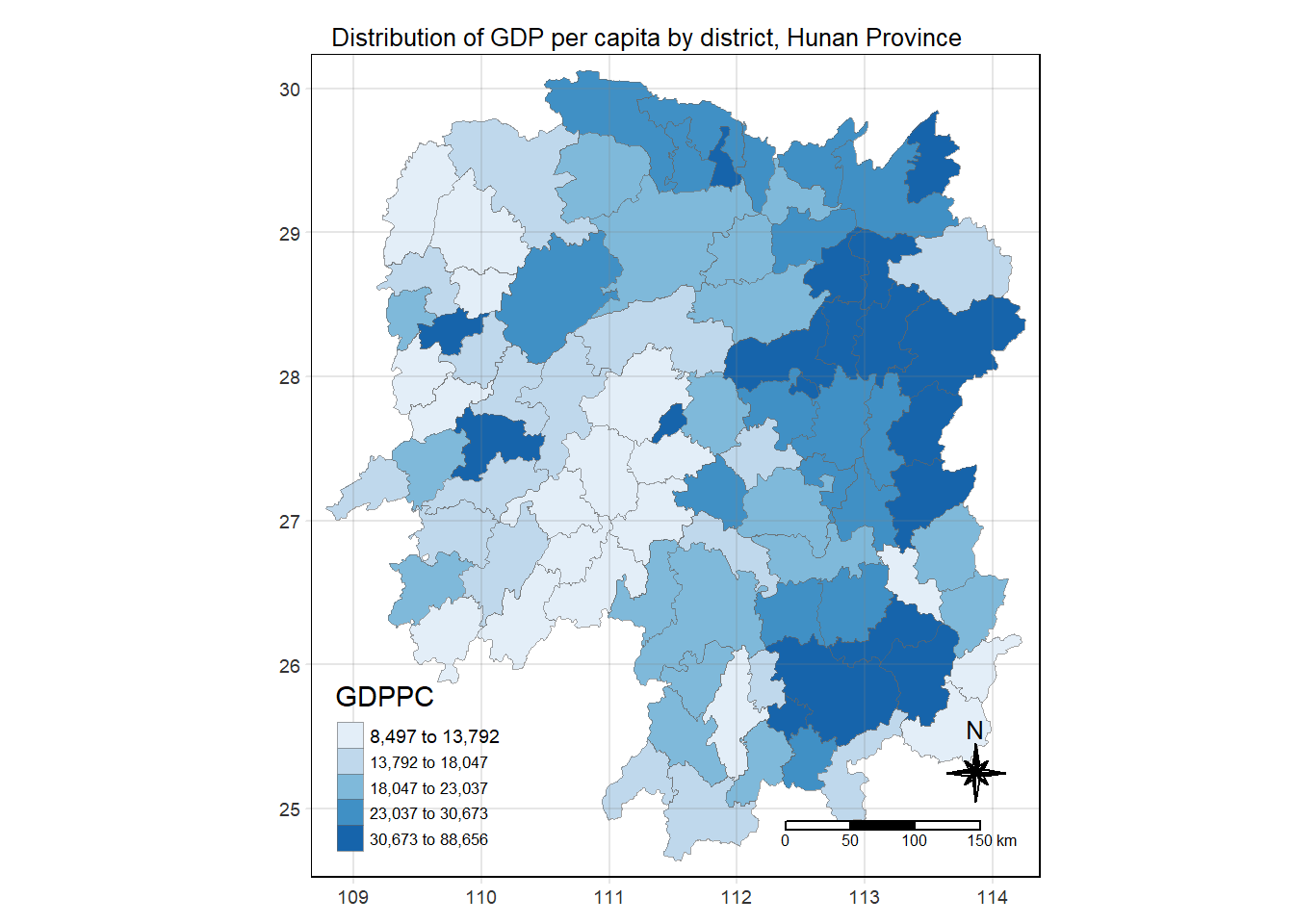
Identify Area (Polygon) Neighbours
Contiguity neighbours method
Queen’s Method
For sf format,
st_contiguity()is used to derive a contiguity neighbour list by using Queen’s Method. Default isqueen = TRUE.For sp format, use spdep’s
poly2nb()(polygon to neighbour) function.dplyr’s
mutate()creates a new fieldnbto store the result ofst_contiguity.before = 1places the new field as the first column
cn_queen <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
.before = 1)Rook’s Method
cn_rook <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb=st_contiguity(geometry, queen = FALSE),
.before = 1)We now know it’s neighbours.
K-Nearest Neighbours
Computing contiguity weights
Distance based method
Contiguity weights: Queen’s Method
wm_q <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry),
wt = st_weights(nb),
.before = 1)Contiguity weights: Rook’s Method
wm_r <- hunan_GDPPC %>%
mutate(nb = st_contiguity(geometry, queen = FALSE),
wt = st_weights(nb),
.before = 1)st_dist_band() lower limit always has to be 0